Find the Direction of the Magnetic Field at Point P
I attached a picture below. What is the direction of magnetic field a point A above the wire carrying current I as shown in the adjoining figure.

Right Hand Rules Determining Magnetic Field Direction Electric Field Magnetic Field Directions
When charges move in a conducting wire and produce a current I the magnetic field at any point P due to the current can be calculated by adding up the magnetic field contributions dB from small segments of the wire G.

. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P due to two 150-mm segments of wire that are opposite each other and each 800 cm 800 cm from. Question From Cengage BM Sharma MAGNETISM AND ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD JEE Main JEE Advanced NEET KVPY AIIMS CBSE RBSE UP. These little Ah the straight pieces on either end arent going to contribute any magnetic field so we can ignore them on again.
The problem asks to find the direction of the magnetic field at point P which is at the center of 2 separate semi-circle wires that form a circle. We use Right Hand Rule - to find the direction of magnetic field due to a solenoid at point is on the axis of the coil. Two parallel wires are 500 cm apart and carry currents in opposite Two parallel wires are 500 cm apart and carry currents in opposite directions as shown in Fig.
C Find the time required for the electron to move from A to B. To find the magnetic field inside a solenoid we will make a simplified model. Magnetic field due to current carrying wire.
A Find the magnitude of the magnetic field that will cause the electron to follow the semicircular path from A to B. View the full answer. I The magnetic field lines produced is into the plane of the paper at R and out of it at S.
Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P due to two 150-mm segments of wire that are opposite each other and each 800 cm from P. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P. It means that when the current flows in a straight wire the magnetic field produced has circular lines of force surrounding the wire having their centres at the wire as shown in fig.
Find the magnitude and direction the magnetic field that will cause the electron follow the semi-circular path from A to B Calculate the time required for the electron move from A to B. The model may differ a little from a real solenoid but the agreement between the two is quite good. The magnitude of the field due to the current element is.
Along the two straight sections of the loop r ˆ and dl are parallel or opposite and thus dl r ˆ 0. Find the magnetic field B at P. 100 7 ratings B magnitude of mag.
We want to find the magnetic field 𝐵at a nearby point P. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P due to the current in the semicircular section of wire shown in Fig. We first mentally divide the wire into differential elements 𝑑𝑠and then define for each element a length vector 𝑑𝑠that has length 𝑑𝑠 and whose direction is the direction of the current in 𝑑𝑠.
View this answer View this answer View this answer done loading. Out of the page. Uh that will give us the current of thie the magnitude of the magnetic field at this point.
The current in each wire flows in the same direction to the right. I 114 A P I2 750 A 0831 m 122 m. Now lets think about the direction again.
What does your expression give when I 1 I 2. Chapter 19 Problem 12MCQ is solved. Iii The current will be going from top to bottom in the wire shown and the magnetic field lines are now in the clockwise direction on.
Well we need to find a magnitude in the direction of the magnetic field at point P. P S SP o Oposite in direction because there is a negative force 5 Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at point P of the figure in terms of I 1 I 2 and R. An electron at point A in the figure has a speed v0 of 150106 ms.
P from this current. Sources of Magnetic Fields 91 Biot-Savart Law Currents which arise due to the motion of charges are the source of magnetic fields. Ii Field at S Field at P Magnetic field strength for a straight current carrying conductor is inversely proportional to the distance from the wire.
Point P_1 At point P_1 the magnetic field due to the wire of radius a is directed to the left and it has a magnitude of mu_0 2I2 pi r mu_0pi Ir The point P_1 is at distances of r-a2 and ra2 from the centers of the two smaller wires. Segment DA is an arc of a circle with radius 200 cm and point P is at its center of curvature. Figure 29-1 shows a wire of arbitrary shape carrying a current 𝑖.
An electron at point A in Figure below has speed Vo of 141x 106 ms. Current-carrying arc Consider the current-carrying loop formed of radial lines and segments of circles whose centers are at point P as shown below. So the magnetic field of the current element is be even by ah bios A were law on so magnetic field.
Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P due to the current in the semicircular section of wire shown below. Find the magnetic field at point P for each of the steady current configurations shown in Figure 53. Calculate the magnetic field magnitude and direction at a point P due to a current I 120 A in the wire shown in Fig.
Solution for Find the magnetic field positive magnitude only no direction at point P. Book 2831 The straight sections of each wire do not create a magnetic field at point P so the only sections that create. To calculate the magnetic field inside the solenoid we will remove the wires on the end and treat the solenoid as infinitely many closely spaced rings.
How do you Determine the Direction of the Magnetic Field. Correct option is C. The two wires will both produce magnetic fields directed to the right with magnitudes of.
B Find the direction of the magnetic field that will cause the electron to follow the semicircular path from A to B. According to the Biot-Savart Law the magnitude of the magnetic field due to a. Unlock a free month of Numerade by answering 20 questions on our new app StudyParty.
Source of Magnetic Fields Worked Examples Example 1. Segment BC is an arc of a circle with radius 300 cm and point P is at the center of curvature of the arc. Does the current in the.
A The total magnetic field at P is the vector sum of the magnetic fields produced by the four segments of the current loop.

What Is The Poynting Vector At The Point P At That Instant Instant Electric Field Point
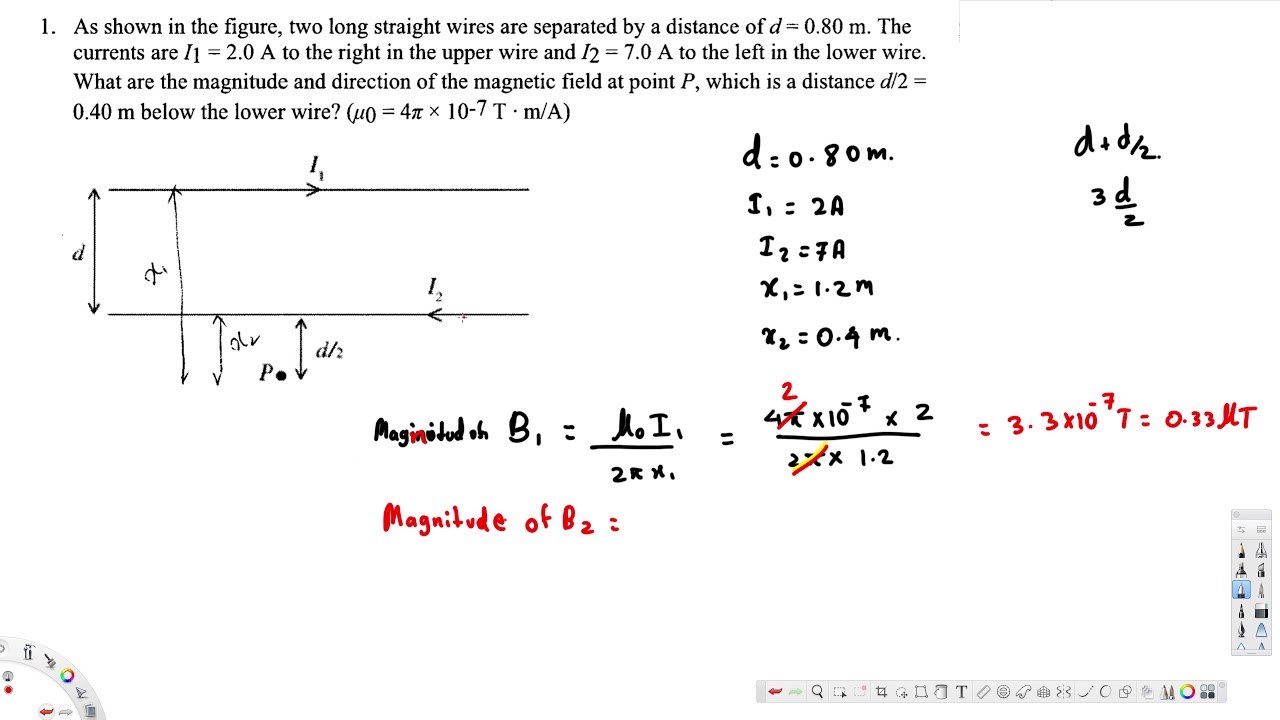
What Are The Magnitude And Direction Of The Magnetic Field At Point P Whic 0 40 M Below The Low Youtube

What Are The Magnitude And Direction Of The Magnetic Field At Point P W Magnetic Field Directions Field
Comments
Post a Comment